Intel Turbo Boost
Intel Turbo Boost是Intel在系列处理器实现的技术,通过动态控制处理器的时钟率来激活处理器运行在超过基础操作主频。
支持不同Turbo Boost版本技术的处理器分为:
- Turbo Boost 1.0: Nehalem
- Turbo Boost 2.0: Sandby Bridge
- Turbo Boost Max 3.0: Ivy Bridge, Haswell, Broadwell, Skylake, Broadwell-E
Turo Boost是在操作系统请求处理器的最高性能状态(highest performance state, pstate)时候激活。
处理器性能状态是通过高级配置和电源接口(Advanced Configuration and Power Interface, ACPI)规范来定义的,这是被所有主流操作系统所支持的开放标准。在Turbo Boost背后的设计概念也被称为"动态超频"。
时钟主频是由处理器电压,电流和热量所限制的,同时也受到当前CPU核心数量和激活核心的最高主频限制。当处理器上负载调用更快性能,并且此时处理器还没有达到上限,则处理器时钟将增加操作频率以满足需求。频率增长,在Nehalem处理器是133MHz,而在Sand Bridge, Ivy Bridge,Haswell和Skylake处理器是100MHz。
Intel Turbo Boost监控处理器当期使用情况,以及处理器是否接近最大热量设计功率(thermal design power, TDP)。这个TDP是处理器支持的最大功率。
Turbo Boost是动态功能,Turbo Boost以133MHz步长增长,直到达到允许的最大Turbo Boost(和处理器型号相关)或者最大TDP。不过,Intel仍然建议处理器工作在基础时钟速度(base clock speed),因为Intel不承诺处理器任何时候都能够达到最大Turbo Boost speed。
Turbo Boost允许一个或多个CPU核心运行在更高的P-states,这个最大P-state需要考虑以下因素:
- 激活的核心数量( C0 或 C1 状态)
- 评估当前处理器消耗(Imax)
- 评估处理器电能消耗(TDP - Thermal Design Power)
- 处理器稳定
Turbo Boot Max 3.0
Intel Turbo Boost Max Technology 3.0 使用一个和CPU中存储信息相连的驱动。它标识并直接工作在最快的芯片内核上。驱动也允许通过白名单自定义配置以便让用户设置应用程序的优先级。这个驱动必须在系统中存在和正确配置,否则操作系统就不能有效路由工作负载到目标处理器核心。
要使用Intel Turbo Boost Max Technology 3.0需要同时满足条件:
- CPU处理器支持 (需要检查Intel CPU功能)
- 操作系统支持
- 驱动和相应的应用软件
- X99或X299主板并使用激活BIOS/firmware支持
和Intel Turbo Boost Technology 2.0不同的是,3.0版本允许单核心更高的主频。
Intel Turbo Boost Max技术的软件用户接口和驱动允许用户优先将负载直接调度到最快的CPU核心上。
支持
Core List是处理器核心的顺序列表,最高性能的core位于最高。更改列表顺序可能会重新以对应性能来表述处理器核心。在操作系统的core序号体系和处理器序号体系相关。例如,Core 0对应逻辑处理器0和1,Core 1对应逻辑处理器2和3。
注意当每个CPU核心最大主频超过时钟 -
Overclocking Enabled显示了Core List的优先级。
Turbo Boost Max技术哈支持设置应用程序可以使用的CPU性能的百分比(阀值),以及评估时间间隔: 默认的评估时间间隔单位是100ms,默认值是10,也就是10x100ms=1s,即每秒评估一次;CPU使用阀值默认是90%,调整这个阀值会降低程序消耗的系统性能。
Intel CPU的P-state, C-state, Turbo Boost
Intel处理器从单核发展到多核提供了在同一个物理CPU核运行2个线程的Hpyer-threading以及Turbo Boost来提供最大性能。处理器核型可以完全关闭(CPU HALT, 主频降到0)来节约电能消耗,并且根据很多因素,如工作负载和问题,来调整处理器核心的工作主频。能耗是现代处理器设计的重要组成。
内核激活Intel P-state
内核启动参数需要激活P-state驱动后才能使用Turbo Boost功能。详细内核参数配置方法参考在Grub2中修改内核启动参数
修改
/etc/default/grub配置行GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX添加intel_idle.max_cstate=1 intel_pstate=enable processor.max_cstate=1执行配置生效
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
安装工具
yum install -y util-linux kernel-tools
| 程序 | 软件包 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| lscpu | util-linux | 查看cpu拓扑 |
| cpupower | kernel-tools | 检查和设置处理器能耗管理、主频等 |
| turbostat | kernel-tools | 监控处理器负载、主频、温度、内存使用等 |
| rdmsr / wrmsr | msr-tools | 读写MSR寄存器 |
检查处理器信息
从/proc/cpuinfo可以获取处理器信息
cat /proc/cpuinfo
输出案例
processor : 23
vendor_id : GenuineIntel
cpu family : 6
model : 45
model name : Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2630 0 @ 2.30GHz
stepping : 7
microcode : 0x710
cpu MHz : 2299.820
cache size : 15360 KB
physical id : 1
siblings : 12
core id : 5
cpu cores : 6
apicid : 43
initial apicid : 43
fpu : yes
fpu_exception : yes
cpuid level : 13
wp : yes
flags : fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush dts acpi mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht tm pbe syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tsc arch_perfmon pebs bts rep_good nopl xtopology nonstop_tsc aperfmperf eagerfpu pni pclmulqdq dtes64 ds_cpl vmx smx est tm2 ssse3 cx16 xtpr pdcm pcid dca sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave avx lahf_lm arat pln pts dtherm tpr_shadow vnmi flexpriority ept vpid xsaveopt
bogomips : 4603.81
clflush size : 64
cache_alignment : 64
address sizes : 46 bits physical, 48 bits virtual
power management:
model name
model name : Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2630 0 @ 2.30GHz 表明处理器型号E5-2630,并且标称主频是2.3GHz。
cpu MHz : 2299.820
cpu MHz : 2299.820是当前处理器核心的主频,注意,单个CPU core有2个HT,CPU core的主频反映在两个HT上都是相同的。可以通过rdmsr从MSR寄存器198H读取处理器当前主频。
检查处理器拓扑
lscpu不带任何参数则显示处理器规格摘要:
Architecture: x86_64
CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit
Byte Order: Little Endian
CPU(s): 24
On-line CPU(s) list: 0-23
Thread(s) per core: 2
Core(s) per socket: 6
Socket(s): 2
NUMA node(s): 1
Vendor ID: GenuineIntel
CPU family: 6
Model: 45
Model name: Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2630 0 @ 2.30GHz
Stepping: 7
CPU MHz: 2300.089
BogoMIPS: 4603.81
Virtualization: VT-x
L1d cache: 32K
L1i cache: 32K
L2 cache: 256K
L3 cache: 15360K
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-23
- 输出处理器表
lscpu -a -e
显示
CPU NODE SOCKET CORE L1d:L1i:L2:L3 ONLINE
0 0 0 0 0:0:0:0 yes
1 0 1 1 1:1:1:1 yes
2 0 0 2 2:2:2:0 yes
3 0 1 3 3:3:3:1 yes
4 0 0 4 4:4:4:0 yes
5 0 1 5 5:5:5:1 yes
6 0 0 6 6:6:6:0 yes
7 0 1 7 7:7:7:1 yes
8 0 0 8 8:8:8:0 yes
9 0 1 9 9:9:9:1 yes
10 0 0 10 10:10:10:0 yes
11 0 1 11 11:11:11:1 yes
12 0 0 0 0:0:0:0 yes
13 0 1 1 1:1:1:1 yes
14 0 0 2 2:2:2:0 yes
15 0 1 3 3:3:3:1 yes
16 0 0 4 4:4:4:0 yes
17 0 1 5 5:5:5:1 yes
18 0 0 6 6:6:6:0 yes
19 0 1 7 7:7:7:1 yes
20 0 0 8 8:8:8:0 yes
21 0 1 9 9:9:9:1 yes
22 0 0 10 10:10:10:0 yes
23 0 1 11 11:11:11:1 yes
可以看到前述/proc/cpuinfo中显示的逻辑处理器24个,实际是12个CPU核心,通过Hyper-threading技术显示为24个逻辑处理器。
要注意处理器核心的物理位置,跨socket调用会延迟性能。
L1d表示L1 data即一级数据缓存;L1i表示L1 instruction即一级指令缓存。也就是一级缓存区分为数据缓存和指令缓存两种。
L2也是CPU核心内使用缓存;L3缓存则是所有物理核心共享的缓存。
P-state
从Linux Kernel 3.9(2009年4月),一个新的intel_pstate加入到内核中,从SandbyBridge处理器开始,后续多代Intel处理器都得到了支持。
intel_pstate驱动支持现代Intel处理器的温控。
处理器P-state是支持处理器运行在不同电压 和/或 主频级别的能力。总的来说,P0是最高性能级别,而P1和P2等依次节约电能但是带来潜在的性能损失。
在Linux内核启动参数中设置intel_pstate=disable选项可以强制使用传统遗留的CPU驱动acpi_cpufreq。
C-state
C-state是idle power saving状态,也就是P-state的相反状态,是执行节电的状态。
当处理器处于P-state状态时,处理器仍然在执行指令;当处理器处于C-state时(除了C0),则处理器是idle状态,也就是没有执行任何指令。
C-state:
C0是操作状态,意味着CPU在做一些有效工作C1是第一个idle状态C2是第二个idle状态:外部I/O控制器Hub阻断发给处理器的中断- 依次类推
当一个逻辑处理器idle是(除了C0以外的C-state),它的主频通常是0(HALT):
cpupower idle-info命令列出支持的C-State:
CPUidle driver: intel_idle
CPUidle governor: menu
Analyzing CPU 0:
Number of idle states: 2
Available idle states: POLL C1-SKX
POLL:
Flags/Description: CPUIDLE CORE POLL IDLE
Latency: 0
Usage: 2667
Duration: 296902700
C1-SKX:
Flags/Description: MWAIT 0x00
Latency: 2
Usage: 776606
Duration: 14056122480
注意:系统必须加载了
intel_idle驱动之后才能使用-m Idle_Stats模块,才能列出支持的C-state,否则输出如下:
$sudo cpupower idle-info
CPUidle driver: none
CPUidle governor: menu
Analyzing CPU 0:
CPU 0: No idle states
cpupower monitor -l可以列出所有可以监控的模块(也就是cpupower monitor输出的所有列可以按照模块来过滤选择)
Monitor "Nehalem" (4 states) - Might overflow after 922000000 s
C3 [C] -> Processor Core C3
C6 [C] -> Processor Core C6
PC3 [P] -> Processor Package C3
PC6 [P] -> Processor Package C6
Monitor "Mperf" (3 states) - Might overflow after 922000000 s
C0 [T] -> Processor Core not idle
Cx [T] -> Processor Core in an idle state
Freq [T] -> Average Frequency (including boost) in MHz
Monitor "Idle_Stats" (2 states) - Might overflow after 4294967295 s
POLL [T] -> CPUIDLE CORE POLL IDLE
C1-S [T] -> MWAIT 0x00
例如,我要监控Idle_Stats (注意大小写)
cpupower monitor -m Idle_Stats
则输出C-state的情况
|Idle_Stats
PKG |CORE|CPU | POLL | C1-S
0| 0| 0| 0.00| 0.00
0| 0| 48| 0.00| 0.00
0| 1| 1| 0.00| 0.00
0| 1| 49| 0.00| 0.00
...
Turbo Boost
- 检查处理器性能
cat /proc/cpuinfo
- 检查处理器主频
cpupower frequency-info
#cpupower frequency-info
analyzing CPU 0:
driver: intel_pstate
CPUs which run at the same hardware frequency: 0
CPUs which need to have their frequency coordinated by software: 0
maximum transition latency: 0.97 ms.
hardware limits: 1000 MHz - 3.10 GHz
available cpufreq governors: performance, powersave
current policy: frequency should be within 1000 MHz and 3.10 GHz.
The governor "powersave" may decide which speed to use
within this range.
current CPU frequency is 2.70 GHz (asserted by call to hardware).
boost state support:
Supported: yes
Active: yes
注意:使用
cpupower frequency-info显示的当前cpu 0主频是一个约数,不精确且有延迟。最好采用cpupower monitor -m Mperf检查能够获取精确的CPU主频,且即使没有使用intel_pstate驱动也能够准确获取频率。
- 检查处理器主频
cpupower monitor -m Mperf
$sudo cpupower monitor -m Mperf
|Mperf
PKG |CORE|CPU | C0 | Cx | Freq
0| 0| 0| 7.85| 92.15| 2820
0| 0| 32| 0.38| 99.62| 2825
0| 1| 1| 42.75| 57.25| 2891
0| 1| 33| 6.98| 93.02| 2890
...
可以看到
Cx显示的就是处理器idle的状态
Turbo Boost MSR
MSR 0x1a0 的第38位用于检查是否激活了Turbo Boost
sudo rdmsr -f 38:38 0x1a0
这里输出值如果是0则表示激活了Turbo Boost,而数值1表示no turbo
如果上述命令不工作,可能需要加载msr内核模块,即执行sudo modprobe msr。
intel_pstate/no_turbo
可以在intel_pstate驱动中关闭turob(设置intel_pstate/no_turbo值为1)
echo 1|sudo tee /sys/devices/system/cpu/intel_pstate/no_turbo
要检查是否启用和停止Turbo,可以通过
cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/intel_pstate/no_turbo来检查
Turbo Boost也可以在运行时通过禁止intel_pstate驱动来关闭:
echo off |sudo tee /sys/devices/system/cpu/intel_pstate/status
注意:这里禁用
intel_pstate之后,处理器主频会跌到物理主频的最小值,此时需要通过MSR寄存器199H来静态设置目标性能状态值(Target performance State Value)
也可以激活intel_pstate驱动:
echo active |sudo tee /sys/devices/system/cpu/intel_pstate/status
注意:这个
intel_pstate/status入口必须在激活Turbo Boost之后才会存在,
读取CPU主频
cpupower提供了frequency-info指令可以读取CPU的主频
cpupower frequency-info
注意,默认没有指定cpu参数则读取cpu 0主频。要读取指定cpu的主频,需要使用-c参数,例如,读取cpu 31的主频
cpupower -c 31 frequency-info
不过,cpupower frequency-info 是通过intel_pstate驱动来获取信息的,所以如果使用 echo off |sudo tee /sys/devices/system/cpu/intel_pstate/status 禁用了intel_pstate驱动,则该指令失效。
可以通过cpupower monitor指令来获取CPU主频,该指令是直接读取MSR 198H 来直接获取CPU主频信息,所以即使禁用了intel_pstate驱动也可以获得准确的数据。
cpupower monitor
输出显示类似
|Nehalem || SandyBridge || Mperf
PKG |CORE|CPU | C3 | C6 | PC3 | PC6 || C7 | PC2 | PC7 || C0 | Cx | Freq
0| 0| 0| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 1.05| 98.95| 2298
0| 0| 12| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 0.00|100.00| 2337
0| 1| 2| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 1.05| 98.95| 2298
0| 1| 14| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 0.03| 99.97| 2299
...
使用turbostat读取主频
turbostat
turbostat默认10秒刷新一次,可以使用-i 1可以1秒刷新一次
CPU Avg_MHz %Busy Bzy_MHz TSC_MHz SMI CPU%c1 CPU%c3 CPU%c6 CPU%c7 CoreTmp PkgTmp PkgWatt RAMWatt PKG_% RAM_%
- 31 1.37 2238 2300 0 98.63 0.00 0.00 0.00 53 53 60.76 12.26 0.00 0.00
0 140 6.12 2289 2300 0 93.88 0.00 0.00 0.00 53 53 31.03 6.04 0.00 0.00
12 0 0.01 1596 2300 0 99.99
2 55 2.42 2254 2300 0 97.58 0.00 0.00 0.00 49
14 5 0.22 2238 2300 0 99.78
4 11 0.48 2185 2300 0 99.52 0.00 0.00 0.00 49
16 0 0.02 1564 2300 0 99.98
6 8 0.34 2258 2300 0 99.66 0.00 0.00 0.00 50
18 0 0.02 1579 2300 0 99.98
8 153 6.70 2281 2300 0 93.30 0.00 0.00 0.00 51
20 0 0.02 1582 2300 0 99.98
10 1 0.05 1961 2300 0 99.95 0.00 0.00 0.00 51
22 0 0.02 1537 2300 0 99.98
1 34 1.53 2216 2300 0 98.47 0.00 0.00 0.00 46 47 29.72 6.22 0.00 0.00
13 2 0.10 2164 2300 0 99.90
3 47 2.17 2183 2300 0 97.83 0.00 0.00 0.00 43
15 2 0.10 2152 2300 0 99.90
5 136 6.18 2206 2300 0 93.82 0.00 0.00 0.00 47
17 0 0.02 1683 2300 0 99.98
7 51 2.29 2234 2300 0 97.71 0.00 0.00 0.00 43
19 0 0.02 1588 2300 0 99.98
9 52 2.34 2209 2300 0 97.66 0.00 0.00 0.00 44
21 0 0.02 1611 2300 0 99.98
11 35 1.57 2219 2300 0 98.43 0.00 0.00 0.00 44
23 2 0.10 1594 2300 0 99.90
这里参数:
Avg_MHz是平均主频,基于APERFBusy%表示处理器繁忙百分比Bzy_MHz是实际的busy frequency,基于MPERFTSC_MHz是固定主频,TSC基于Time Stamp Counter
APERF(average) andMPERF(maximum) 是MSR寄存器可以提供当前CPU主频信息。
/proc/cpuinfo中的主频信息
在/proc/cpuinfo中有一个信息是cpu MHz
在2016年4月,Len Brown发布的patch修改了cpuinfo中计算主频的方法,采用了APERF和MPERF MSR来计算CPU主频:Calculate MHz using APERF/MPERF for cpuinfo and scaling_cur_freq
操作系统启动时,在系统日志中记录了TSC主频:
dmesg|grep 'MHz processor'
显示输出
[ 0.000000] tsc: Detected 2493.598 MHz processor
cpupower工具获取主频
cpupower工具提供了多种方法读取处理器主频:
sudo cpupower monitor -m 'Mperf'
输出
|Mperf
PKG |CORE|CPU | C0 | Cx | Freq
0| 0| 0| 99.54| 0.46| 2693
0| 0| 48| 99.54| 0.46| 2693
0| 1| 1| 99.54| 0.46| 2693
0| 1| 49| 99.54| 0.46| 2693
...
如果启用了
intel_pstate,也可以通过for core in $(seq 0 31); do sudo cpupower -c $core frequency-info|grep 'current CPU'; done(假设这里服务器是32个HT)
rdmsr/wrmsr
- Intel处理器的MSR中性能状态值:目标性能状态值
Target performance State Value(199H)和当前性能状态值Current performance State Value
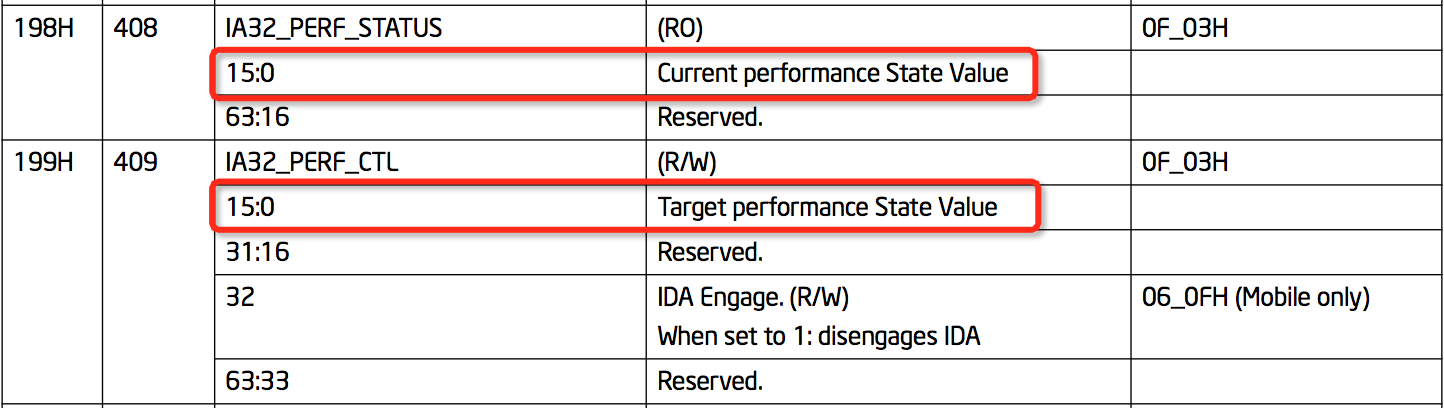
- 读取MSR寄存器
# 当前性能状态值
sudo rdmsr --bitfield 15:0 -a 0x199
# 设置的性能状态值
sudo rdmsr --bitfield 15:0 -a 0x198
读取的值需要乘以
100才是实际的值。例如,198H值1900表示值是(1x16+9)x100=2500(2.5GHz),198H值1b00表示值是(1x16+11)x100=2700(2.7GHz)。
- 禁用
intel_pstate驱动:要通过wrmsr工具调整199HMSR,需要确保停用intel_pstate驱动,否则调整值会被intel_pstate驱动自动覆盖无法生效。
echo off | sudo tee /sys/devices/system/cpu/intel_pstate/status
- 要调整主频需要通过
wrmsr写入MSR寄存器
wrmsr使用参考 wrmsr
sudo wrmsr -p 0 0x199 0x1a00
wrmsr只支持-p(指定处理器)和-a(所有处理器)参数
- 然后检查性能设置值
#sudo $msr_cmd_dir/rdmsr --bitfield 15:0 -a 0x199
1a00
1900
1900
检查性能当前值可以看到和设置值一致
#sudo $msr_cmd_dir/rdmsr --bitfield 15:0 -a 0x198
1a00
1900
1900
检查主频,可以看到cpu 0/12增加了100MHz,达到了2.6GHz
#cpupower monitor
|Nehalem || Mperf || Idle_Stats
PKG |CORE|CPU | C3 | C6 | PC3 | PC6 || C0 | Cx | Freq || POLL | C1-S
0| 0| 0| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 99.92| 0.08| 2593|| 0.00| 0.00
0| 0| 12| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 99.92| 0.08| 2593|| 0.00| 0.00
0| 1| 1| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 99.92| 0.08| 2494|| 0.00| 0.00
0| 1| 13| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 99.92| 0.08| 2493|| 0.00| 0.00
...
此时可以不断通过修改199H MSR实现处理器主频调整。
- 最后,测试完成后恢复
intel_pstate驱动
echo active |sudo tee /sys/devices/system/cpu/intel_pstate/status
神
测试
在上述调整处理器主频过程中,可以通过脚本不断压测处理器,以得到处理器主频值。
- 性能测试可以通过计算pi来实现,以下
scale=20000表示计算pi的精度是2万位:
time echo "scale=20000; 4*a(1)" | bc -l -q
- 如果要压所有的CPU满负荷,以确定Trubo Boost主频,可以采用如下
yes.sh脚本
nohup yes > /dev/null &
然后启用对24核服务器压测,每个脚本都通过taskset指令绑定到独立CPU上
for i in `seq 0 23`;do taskset -c $i sh ./yes.sh;done
对于进程pid,可以采用
taskset -cp <cpu N> <pid>来设置进程<pid>到处理器<cpu N>运行。
异常排查
- 系统内核明确设置了
intel_pstate=enable但是启动之后,依然出现如下报错
#cpupower frequency-info
analyzing CPU 0:
no or unknown cpufreq driver is active on this CPU
#cpupower info
System does not support Intel's performance bias setting
analyzing CPU 0:
BIOS开启turbo没有成功导致。
参考
- Intel Turbo Boost
- Frequently Asked Questions about Intel® Turbo Boost Max Technology 3.0
- How Intel Turbo Boost Works
- Intel CPUs: P-state, C-state, Turbo Boost, CPU frequency, etc.
- Balancing Power and Performance in the Linux Kernel - Intel开源中心提供的有关能耗和性能平衡的介绍文档
- Suse doc: System Analysis and Tuning Guide > Power Management